

Sagittal alignment of the first metatarsal varies greatly because of the rheumatoid midfoot and hindfoot deformities. The mean value of the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society and Japanese Society for Foot Surgery clinical scores significantly improved overall, except for 2 patients (10%), who complained of first toe pain at the final follow-up visit owing to sagittal misalignment of the fused first MTP joint. All first MTP joints and first metatarsal bones were fused successfully. When the bones, ligaments, and tendons in an MTP joint are exposed to high pressure. The mean duration of follow-up was 7.9 (range 4 to 13) years. The metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints are the links between your toes and the bones in the main part of your foot. Symptomatic radiographic foot OA affects 17 of adults aged 50 years and over. Most existing studies focus on the first metatarsophalangeal joint, with evidence relating to midfoot OA being particularly sparse. We retrospectively evaluated the postoperative clinical outcomes and radiographic findings for 16 consecutive female patients (20 feet) with symptomatic rheumatoid forefoot deformities. Foot osteoarthritis (OA) is a common problem in older adults yet is under-researched compared to knee or hand OA.
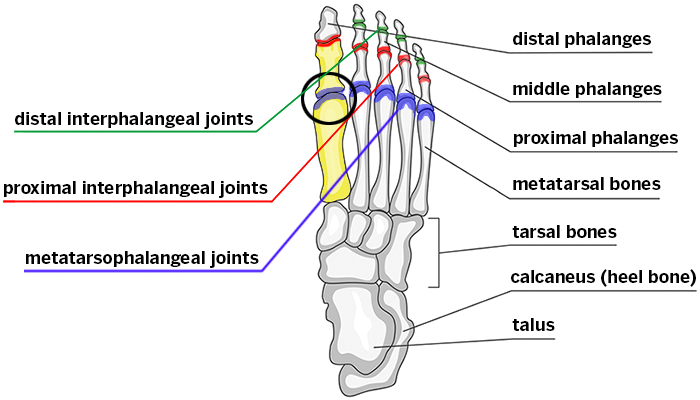
Special focus was placed on the sagittal alignment of the first metatarsophalangeal joint after arthrodesis. The present study assessed the midterm results of reconstruction for rheumatoid forefoot deformity with arthrodesis of the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, scarf osteotomy, resection arthroplasty of the metatarsal head of the lesser toes, and surgical repair of hammertoe deformity (arthrodesis of the proximal interphalangeal joint).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
